Emulating Smoke Transport Between Canada and NYC Using a Graph Neural Network
By Peyton Braun, Texas A&M uNIVERSITY
Advisors: Kang Sun, CSEE, University at Buffalo
Advisors: Stuart Evans, GEOGRAPHY, University at Buffalo
Project Objectives
•What caused the smoke transport in the June 2023 Canadian wildfires?
•How can we use a graph neural network to emulate wildfire smoke transport?
•Smoke plumes degrade air quality, which is particularly important in heavily populated areas such as New York City.
Data and Results
•Data from GEOS-CF, a high-resolution model which combines the GEOS meteorological forecasting model and the GEOS-Chem atmospheric chemistry module.
•Identified and analyzed a couple fires of interest using the GEOS-CF data.
•Preliminary training and evaluation of a graph neural network.
Significance
•Machine learning is quickly becoming the future of modeling and is much more accessible to a broader community than traditional numerical modeling.
•Next steps include continuing to train and test the GNN, as well as improving it to take inputs from both real-world and model data.
Publication or Conference
Attending and presenting at AGU 2025.
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Center for Geological and Climate Hazards
Interdisciplinary Research Experience for Undergraduates in Atmospheric and Geological Hazards
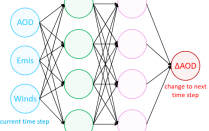
Illustration of a simple neural network, where the inputs include AOD, emissions, and winds, and the output is the change of AOD to the next time step.